sábado, 25 de mayo de 2013
Formalism: Noam Chomsky
14:27
No comments
Formal language theory, the discipline which studies
formal grammar and language, is a branch of applied mathematics.
Its applications are found in theoretical computer
science, theoretical linguistics, formal semantics, mathematical logic, and
other areas.
Formalism or generative grammar is the third
predominant linguistic school of the twentieth century. This theory is mostly
influence by Noam Chomsky and his concept of generative grammar, which was
firstly presented in Syntactic Structures (1957).
Avram Noam Chomsky is an American linguist,
philosopher, cognitive scientist, logician, historian, political critic, and
activist. He is an Institute Professor and Professor (Emeritus) in the
Department of Linguistics & Philosophy at MIT, where he has worked for over
50 years. In addition to his work in linguistics, he has written on war,
politics, and mass media, and is the author of over 100 books. Chomsky has been
described as the "father of modern linguistics and a major figure of
analytic philosophy. His work has influenced fields such as computer science,
mathematics, and psychology. He is credited as the creator or co-creator of the
Chomsky hierarchy, the universal grammar theory, and the Chomsky–Schützenberger
theorem.
The linguistic formalism derived from Chomsky can be
characterized by a focus on innate universal grammar, and a disregard for the
role of stimuli.
The formalism concentrates on the set of rules a
language has (competence), and not on the usage of this set when producing
phrases (performance). Competence is determined on the basis of an abstract
ideal speaker of language. Hence, there is no analysis of empirical data or
corpora. Whereas language in functionalist approaches is contemplated as a
"tool" with communicative functions, it is considered as "a
setof sentences" in formalism.
Chomsky´s competence-performance distinction led to
his formal approach. The formal approach focuses on the structure of the
language, emphasizing the deductive properties of the language system
(generative rules, algorithms): looking patterns within the linguistics
elements.
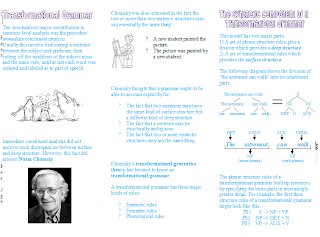
A generative grammar is a system of explicit rules
that assign to each sequence of phones, whetherof the observed corpus or not, a
structural description that contains all information about how this sequence of
phones is represented on each of the several linguistic levels - in particular,
information as to whether this sequence of phones is a properly formed or
grammatical sentence.ACTIVITY
Suscribirse a:
Comentarios (Atom)